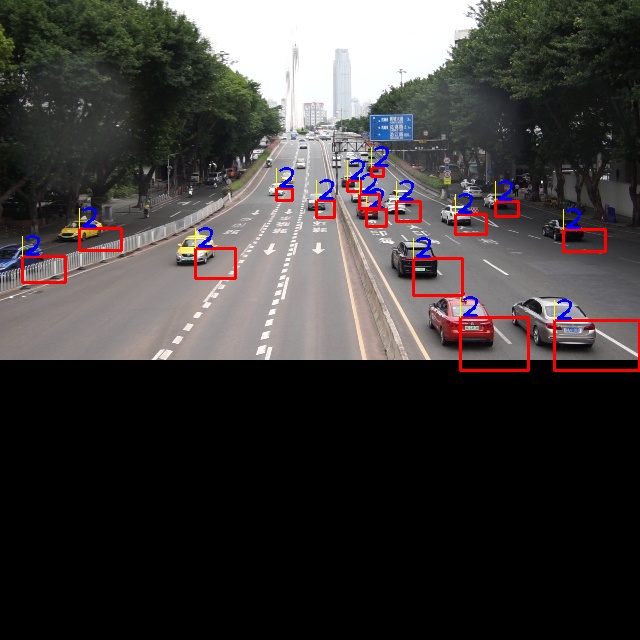
这段python 代码作做主要是为了对图片进行尺寸、和输入数据统一化的处理。yolov5的输入一般是640×640 的尺寸 是以 NCHW 的布局排列,其中N 是批次数 一船是1 ,C是通道数一般是3 (代表RGB 三个通道),H是 height 高度,W是width 宽度,所以这个代码主要作用是为了把图片的长,宽转成640×640。然后把图片转为numpy 数组,增加一个批次维度,然后再把数组的shaep 即布局转为 NCHW 即[1,3,640,640]
但从这个代码看,他并没有考虑图像的长宽比因为resize 的强行处理,被强行扭曲了。这将导致图像的内容会被压扁扭曲了。在一般的模型,包括官方的,或者使用自行标注的数据集,都不会使用这样扭曲了的图像进行训练。需要某些时候会使用一些方法对原始采集的图片进行一些人工处理凭空造一些数据。但这么扭曲压扁的是比较少的。所以,这么对输入图像进行处理是会造成模型识别结果不正确的问题。这是问题其一。
atc –model=./yolov5s_v6.2.onnx –framework=5 –input_shape=”images:1,3,640,640″ –output=v5s_o –soc_version=”OPTG” –output_type=FP32
其三,也是最后的坑,即使修改这个python 程序,把RGB 的转换去掉了,再把图像resize 这个处理改掉,保持原图模宽比。但最后输出的.bin 文件,再调用官方的库读进去处理,模型识别的结果还是错的。原因,目前还不明,估计是保存或读取文件到内存的方式哪里不对导致最后读进去处理,输入到模型的数据是错的。在这个问题是我花了大量的时间来调试代码。一开始以为是后处理代码的问题,怎么都不对。然后才怀疑前处理的数据问题。最后,解决方法是,直接不要官方的这个python 代码生成.bin 文件,把他这个处理,直接使用c++重写。然后,把处理后数据直接输入到 ACL 库的对应输入数据函数。然后,调用ACL库进行模型推理。
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstring>
#include <sys/time.h>
using namespace std;
#include “acl/acl.h”
#include “opencv2/opencv.hpp”
#define INFO_LOG(fmt, …) fprintf(stdout, “[INFO] ” fmt “\n”, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define WARN_LOG(fmt, …) fprintf(stdout, “[WARN] ” fmt “\n”, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define ERROR_LOG(fmt, …) fprintf(stderr, “[ERROR] ” fmt “\n”, ##__VA_ARGS__)
typedef enum Result {
SUCCESS=0,
FAILED=1
} Result;
bool g_isDevice = false;
const char *aclConfigPath = “acl.json”;
const char *MODEL_PATH=”model/v5s.om”;
// const char *PIC=”data/t_yolov5.bin”;
const char *PIC=”data/output2.jpg”;
const int loop_count=11;
// YOLOv5 相关参数
const int INPUT_SIZE = 640;
const float CONF_THRESHOLD = 0.5;
const float NMS_THRESHOLD = 0.45;
const int NUM_CLASSES = 80;
const float OBJ_THRESH = 0.5;
const float NMS_THRESH = 0.4;
// 定义检测框结构体
struct Box {
floatx, y, w, h,x1,y1,x2,y2;
floatscore;
floatconfidence;
floatclass_score;
intclass_id;
};
// 定义检测结果结构体
struct Detection {
Boxbox;
floatscore;
intclass_id;
};
// 定义NMS输出结构
struct DetectionResult {
floatx, y, w, h; // 中心点坐标和宽高
floatprob; // 最终概率
intobj_id; // 类别ID
};
// 定义检测框结构
struct bbox_t {
cv::Rectbox;
floatx, y, w, h;
floatscore;
floatprob;
intobj_id;
intclass_id;
};
// sigmoid激活函数
inline float sigmoid(float x) {
return1.0f/ (1.0f+expf(-x));
}
/// <summary>
/// preprocess image
/// </summary>
/// <param name=”image”></param>
/// <param name=”target_size”></param>
/// <returns></returns>
cv::Mat preprocess_image(const cv::Mat& frame) {
// Format frame
intw=frame.cols;
inth=frame.rows;
int_max=std::max(h, w);
cv::Matimage=cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(_max, _max), CV_8UC3);
cv::Rectroi(0, 0, w, h);
frame.copyTo(image(roi));
// Fix bug, boxes consistency!
floatx_factor=image.cols/static_cast<float>(640);
floaty_factor=image.rows/static_cast<float>(640);
cv::Matblob=cv::dnn::blobFromImage(image, 1/255.0, cv::Size(640, 640), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
// size_t tpixels = model_session.input_model_height * model_session.input_model_width * 3;
// std::array<int64_t, 4> input_shape_info{ 1, 3, model_session.input_model_height, model_session.input_model_width };
// return { blob, tpixels, input_shape_info, x_factor, y_factor };
returnblob;
}
// 计算两个边界框的IoU(交并比)
float calculateIoU(const Box& box1, const Box& box2) {
floatx1=std::max(box1.x1, box2.x1);
floaty1=std::max(box1.y1, box2.y1);
floatx2=std::min(box1.x2, box2.x2);
floaty2=std::min(box1.y2, box2.y2);
floatintersection_area=std::max(0.0f, x2-x1) *std::max(0.0f, y2-y1);
floatbox1_area= (box1.x2-box1.x1) * (box1.y2-box1.y1);
floatbox2_area= (box2.x2-box2.x1) * (box2.y2-box2.y1);
floatunion_area=box1_area+box2_area-intersection_area;
returnintersection_area/union_area;
}
// 计算IOU
float calculate_iou(const Box& box1, const Box& box2) {
// 计算每个框的左上角和右下角坐标
floatx1_min=box1.x-box1.w/2;
floaty1_min=box1.y-box1.h/2;
floatx1_max=box1.x+box1.w/2;
floaty1_max=box1.y+box1.h/2;
floatx2_min=box2.x-box2.w/2;
floaty2_min=box2.y-box2.h/2;
floatx2_max=box2.x+box2.w/2;
floaty2_max=box2.y+box2.h/2;
// 计算交集区域
floatinter_x_min=std::max(x1_min, x2_min);
floatinter_y_min=std::max(y1_min, y2_min);
floatinter_x_max=std::min(x1_max, x2_max);
floatinter_y_max=std::min(y1_max, y2_max);
floatinter_width=std::max(0.0f, inter_x_max-inter_x_min);
floatinter_height=std::max(0.0f, inter_y_max-inter_y_min);
floatinter_area=inter_width*inter_height;
// 计算并集区域
floatbox1_area=box1.w*box1.h;
floatbox2_area=box2.w*box2.h;
floatunion_area=box1_area+box2_area-inter_area;
// 计算IOU
returninter_area/union_area;
}
// 非极大值抑制
std::vector<Box> nonMaxSuppression(const std::vector<Box>& boxes, float threshold) {
std::vector<Box>result;
if (boxes.empty()) returnresult;
// 按置信度降序排列边界框
std::vector<Box>sorted_boxes=boxes;
std::sort(sorted_boxes.begin(), sorted_boxes.end(),
[](const Box& a, const Box& b) {
returna.score>b.score;
});
std::vector<bool>is_removed(sorted_boxes.size(), false);
for (size_ti=0; i<sorted_boxes.size(); ++i) {
if (is_removed[i]) continue;
result.push_back(sorted_boxes[i]);
// 移除与当前框IoU较高的其他框
for (size_tj=i+1; j<sorted_boxes.size(); ++j) {
if (is_removed[j]) continue;
// 只比较同一类别的边界框
if (sorted_boxes[i].class_id==sorted_boxes[j].class_id) {
floatiou=calculateIoU(sorted_boxes[i], sorted_boxes[j]);
if (iou>=threshold) {
is_removed[j]=true;
}
}
}
}
returnresult;
}
// 计算 IOU(交并比)
float iou(const Box& a, const Box& b) {
floatinterArea=std::max(0.0f, std::min(a.x+a.w, b.x+b.w) -std::max(a.x, b.x)) *
std::max(0.0f, std::min(a.y+a.h, b.y+b.h) -std::max(a.y, b.y));
floatunionArea=a.w*a.h+b.w*b.h-interArea;
returninterArea/unionArea;
}
// 非极大值抑制
std::vector<Detection> nms(const std::vector<Detection>& detections, float iou_threshold) {
std::vector<Detection>result;
std::vector<bool>suppressed(detections.size(), false);
for (size_ti=0; i<detections.size(); ++i) {
if (suppressed[i]) continue;
result.push_back(detections[i]);
for (size_tj=i+1; j<detections.size(); ++j) {
if (iou(detections[i].box, detections[j].box) >iou_threshold) {
suppressed[j]=true;
}
}
}
returnresult;
}
void draw_boxes(cv::Mat& image, const std::vector<DetectionResult>& boxes) {
for(size_ti=0; i<boxes.size(); i++) {
intidx=boxes[i].obj_id;
cv::Rectrect={(int)boxes[i].x,(int)boxes[i].y,(int)boxes[i].w,(int)boxes[i].h};
cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8);
cv::rectangle(image, cv::Point(boxes[i].x, boxes[i].y-20),
cv::Point(boxes[i].x, boxes[i].y), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 255), -1);
putText(image, to_string(idx), cv::Point(boxes[i].x, boxes[i].y), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 2.0, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8);
}
}
vector<cv::Rect> xywh2xyxy(const vector<cv::Rect2f> &boxes) {
vector<cv::Rect>output_boxes;
for (constauto&box : boxes) {
floatx1=box.x-box.width/2.0;
floaty1=box.y-box.height/2.0;
floatx2=box.x+box.width/2.0;
floaty2=box.y+box.height/2.0;
output_boxes.emplace_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(x1, y1), cv::Point(x2, y2)));
}
returnoutput_boxes;
}
// 过滤低置信目标
void filter_boxes(vector<vector<float>> &boxes, vector<float> &confidences, vector<int> &class_ids) {
vector<vector<float>>filtered_boxes;
vector<float>filtered_confidences;
vector<int>filtered_classes;
for (size_ti=0; i<confidences.size(); i++) {
if (confidences[i]>=OBJ_THRESH) {
filtered_boxes.push_back(boxes[i]);
filtered_confidences.push_back(confidences[i]);
filtered_classes.push_back(class_ids[i]);
}
}
boxes=filtered_boxes;
confidences=filtered_confidences;
class_ids=filtered_classes;
}
// NMS 非极大值抑制
std::vector<DetectionResult> nms_boxes(const std::vector<Box>& boxes,
floatnms_threshold,
floatconf_threshold) {
std::vector<DetectionResult>result;
// 准备OpenCV NMS所需的数据结构
std::vector<int>classIds;
std::vector<float>confidences;
std::vector<cv::Rect>cv_boxes;
// 遍历所有检测框
for (constauto&box : boxes) {
// 计算最终得分
floatscore=box.confidence*box.class_score;
// 应用置信度阈值
if (score>conf_threshold) {
// 转换为左上角和宽高表示
floatx1=box.x-box.w/2;
floaty1=box.y-box.h/2;
floatw=box.w;
floath=box.h;
// 确保在有效范围内
x1=std::max(0.0f, x1);
y1=std::max(0.0f, y1);
// 添加到列表
classIds.push_back(box.class_id);
confidences.push_back(score);
cv_boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(x1, y1, w, h));
}
}
// 应用NMS
std::vector<int>indices;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(cv_boxes, confidences, conf_threshold, nms_threshold, indices);
std::cout<<“NMS前有效框数量: “<<cv_boxes.size() <<“, NMS后保留: “<<indices.size() <<std::endl;
// 构建输出结果
for (size_ti=0; i<indices.size(); ++i) {
intidx=indices[i];
DetectionResultdet;
det.x=cv_boxes[idx].x+cv_boxes[idx].width/2; // 转回中心点表示
det.y=cv_boxes[idx].y+cv_boxes[idx].height/2;
det.w=cv_boxes[idx].width;
det.h=cv_boxes[idx].height;
det.prob=confidences[idx];
det.obj_id=classIds[idx];
result.push_back(det);
}
returnresult;
}
// 在图像上绘制检测框
void drawDetectionResults(cv::Mat& image, const std::vector<Box>& detections) {
// 定义颜色表 – 为不同类别分配不同颜色
conststd::vector<cv::Scalar>colors= {
cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), // 蓝色
cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), // 绿色
cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), // 红色
cv::Scalar(255, 255, 0), // 青色
cv::Scalar(0, 255, 255), // 黄色
cv::Scalar(255, 0, 255), // 紫色
cv::Scalar(128, 0, 0), // 深蓝
cv::Scalar(0, 128, 0), // 深绿
cv::Scalar(0, 0, 128), // 深红
cv::Scalar(128, 128, 0) // 橄榄
};
// 类别名称,根据您的模型调整
conststd::vector<std::string>class_names= {
“person”, “bicycle”, “car”, “motorcycle”, “airplane”, “bus”, “train”, “truck”, “boat”,
“traffic light”, “fire hydrant”, “stop sign”, “parking meter”, “bench”, “bird”, “cat”,
“dog”, “horse”, “sheep”, “cow”, “elephant”, “bear”, “zebra”, “giraffe”, “backpack”,
“umbrella”, “handbag”, “tie”, “suitcase”, “frisbee”, “skis”, “snowboard”, “sports ball”,
“kite”, “baseball bat”, “baseball glove”, “skateboard”, “surfboard”, “tennis racket”,
“bottle”, “wine glass”, “cup”, “fork”, “knife”, “spoon”, “bowl”, “banana”, “apple”,
“sandwich”, “orange”, “broccoli”, “carrot”, “hot dog”, “pizza”, “donut”, “cake”, “chair”,
“couch”, “potted plant”, “bed”, “dining table”, “toilet”, “tv”, “laptop”, “mouse”,
“remote”, “keyboard”, “cell phone”, “microwave”, “oven”, “toaster”, “sink”, “refrigerator”,
“book”, “clock”, “vase”, “scissors”, “teddy bear”, “hair drier”, “toothbrush”
};
// 遍历所有检测框
for (constauto&det : detections) {
// 获取边界框坐标
intx1=static_cast<int>(det.x1);
inty1=static_cast<int>(det.y1);
intx2=static_cast<int>(det.x2);
inty2=static_cast<int>(det.y2);
// 确保边界框在图像范围内
x1=std::max(0, std::min(x1, image.cols-1));
y1=std::max(0, std::min(y1, image.rows-1));
x2=std::max(0, std::min(x2, image.cols-1));
y2=std::max(0, std::min(y2, image.rows-1));
// 计算颜色索引
intcolor_idx=det.class_id%colors.size();
cv::Scalarcolor=colors[color_idx];
// 绘制矩形框
cv::rectangle(image, cv::Point(x1, y1), cv::Point(x2, y2), color, 2);
// 准备标签文本
std::stringclass_name= (det.class_id<class_names.size()) ?
class_names[det.class_id]:
“class “+std::to_string(det.class_id);
std::stringlabel=class_name+” “+std::to_string(static_cast<int>(det.score*100)) +”%”;
// 绘制填充的矩形作为标签背景
intbaseline=0;
cv::Sizelabel_size=cv::getTextSize(label, cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseline);
cv::rectangle(image,
cv::Point(x1, y1-label_size.height-5),
cv::Point(x1+label_size.width, y1),
color, -1);
// 绘制文本标签
cv::putText(image, label, cv::Point(x1, y1-5),
cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), 1);
}
}
// —————– 解析 ACL 输出为 C++ 数据 —————–
vector<cv::Mat> parseAclOutput(aclmdlDataset *dataset) {
vector<cv::Mat>outputs;
size_tnum_tensors=aclmdlGetDatasetNumBuffers(dataset);
for (size_ti=0; i<num_tensors; ++i) {
aclDataBuffer*buffer=aclmdlGetDatasetBuffer(dataset, i);
void*data=aclGetDataBufferAddr(buffer);
size_tbuffer_size=aclGetDataBufferSizeV2(buffer);
// 获取 shape (1, 255, 80, 80) / (1, 255, 40, 40) / (1, 255, 20, 20)
size_tgrid_size= (i==0) ?80: (i==1) ?40:20;
intnum_anchors=3;
intnum_classes=80;
intchannels=num_anchors* (num_classes+5); // 255 = 3 * (80 + 5)
float*float_data=reinterpret_cast<float*>(data);
// 创建 OpenCV Mat 格式: (grid_size, grid_size, channels)
cv::Matmat(grid_size*grid_size, channels, CV_32F, float_data);
// 复制数据,确保 ACL 释放后仍可用
cv::Matmat_clone=mat.clone();
outputs.push_back(mat_clone);
}
returnoutputs;
}
void postprocess(cv::Mat& frame, cv::Mat boxes_m, cv::Mat confs_m,float conf_threshold, float nms_threshold, std::vector<Detection>& final_detections){
intnum_boxes=boxes_m.rows;
intnum_classes=confs_m.cols;
std::vector<Detection>boxes;
std::vector<cv::Rect>boxes_list;
std::vector<float>conf_list;
std::vector<int>class_id_list;
floatscale_x=1920/416.0f;
floatscale_y=1080/416.0f;
// 遍历所有框
for (inti=0; i<num_boxes; ++i) {
// 获取框坐标
Boxrect{boxes_m.at<float>(i, 0)*416, boxes_m.at<float>(i, 1)*416,
boxes_m.at<float>(i, 2)*416, boxes_m.at<float>(i, 3)*416};
rect.x=std::max(0.0f, rect.x*scale_x);
rect.y=std::max(0.0f, rect.y*scale_y);
rect.w=std::max(0.0f, (rect.w*scale_x)-rect.x);
rect.h=std::max(0.0f, (rect.h*scale_y)-rect.y);
// 获取该框的最大类别置信度
intclass_id=-1;
floatmax_conf=0.0f;
for (intj=0; j<num_classes; ++j) {
floatconf=confs_m.at<float>(i, j);
if (conf>max_conf) {
max_conf=conf;
class_id=j;
}
}
// Detection det;
// 将框和置信度存入结构体
// boxes.push_back({rect, max_conf, class_id});
boxes_list.push_back({rect.x,rect.y,rect.w,rect.h});
conf_list.push_back(max_conf);
class_id_list.push_back(class_id);
}
for(autobox:boxes){
cout<<“Box “<<“: [“<<box.box.x<<“, “<<box.box.y<<“, “<<box.box.w<<“, “<<box.box.h<<“]”<<endl;
}
cout<<“num_boxes: “<<num_boxes<<endl;
cout<<“num_classes: “<<num_classes<<endl;
std::vector<int>indices;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes_list, conf_list, conf_threshold, nms_threshold, indices);
for (intidx : indices) {
Detectiondet;
det.box.x=boxes_list[idx].x;
det.box.y=boxes_list[idx].y;
det.box.w=boxes_list[idx].width;
det.box.h=boxes_list[idx].height;
det.class_id=class_id_list[idx];
det.score=conf_list[idx];
boxes.push_back(det);
}
// // 调用非极大值抑制进行后处理
// float iouThreshold = 0.5f;
// float confThreshold = 0.5f;
// std::vector<Detection> finalBoxes = nonMaximumSuppression(boxes, iouThreshold, confThreshold);
// // 输出最终保留的框
std::cout<<“Final Detected Boxes after NMS: “<<boxes.size() <<std::endl;
for (constauto&box : boxes) {
std::cout<<“Box “<<“: [“<<box.box.x<<“, “<<box.box.y<<“, “<<box.box.w<<“, “<<box.box.h<<“]”<<“, Confidence: “<<box.score<<“, Class: “<<box.class_id<<std::endl;
}
// draw_boxes(frame,boxes);
}
void processFeatureMap(const float* feature_map, std::vector<Box>& detections,
intgrid_h, intgrid_w, intnum_anchors, intnum_outputs,
floatconf_threshold, intinput_w, intinput_h) {
// YOLOv5 v6.2 anchors和strides
std::vector<std::vector<int>>anchors= {
{10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23}, // 80×80
{30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119}, // 40×40
{116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326} // 20×20
};
intstrides[] = {8, 16, 32}; // 对应80×80, 40×40, 20×20
// 确定当前特征图对应的索引
intfeature_idx=0;
if (grid_h==80) feature_idx=0;
elseif (grid_h==40) feature_idx=1;
elseif (grid_h==20) feature_idx=2;
else {
std::cout<<“Unsupported feature map size: “<<grid_h<<“x”<<grid_w<<std::endl;
return;
}
intstride=strides[feature_idx];
intnum_classes=num_outputs-5; // 85 – 5 = 80类
// 调试信息
std::cout<<“处理特征图: “<<grid_h<<“x”<<grid_w
<<” stride=”<<stride
<<” anchor_group=”<<feature_idx<<std::endl;
intdebug_count=0; // 用于限制调试输出
// 遍历每个anchor、每行、每列
for (inta=0; a<num_anchors; ++a) {
for (inti=0; i<grid_h; ++i) {
for (intj=0; j<grid_w; ++j) {
// 计算当前网格点在特征图中的索引
// 对应 record 变量的计算
float*record=const_cast<float*>(feature_map) +
a*grid_h*grid_w*num_outputs+
i*grid_w*num_outputs+
j*num_outputs;
// 指向类别分数的指针
float*cls_ptr=record+5;
// 遍历所有类别
for (intcls=0; cls<num_classes; ++cls) {
// 计算类别置信度 = sigmoid(类别分数) * sigmoid(objectness)
floatscore=sigmoid(cls_ptr[cls]) *sigmoid(record[4]);
// 只处理高于阈值的检测结果
if (score>conf_threshold) {
// 解码边界框坐标
floatcx= (sigmoid(record[0]) *2.0f-0.5f+j) *stride;
floatcy= (sigmoid(record[1]) *2.0f-0.5f+i) *stride;
floatw=pow(sigmoid(record[2]) *2.0f, 2) *anchors[feature_idx][2*a];
floath=pow(sigmoid(record[3]) *2.0f, 2) *anchors[feature_idx][2*a+1];
// 创建Box对象并保存检测结果
Boxbox;
box.x=cx; // 中心x坐标
box.y=cy; // 中心y坐标
box.w=w; // 宽度
box.h=h; // 高度
box.confidence=sigmoid(record[4]); // objectness
box.class_id=cls; // 类别ID
box.class_score=sigmoid(cls_ptr[cls]); // 类别置信度
// 添加到检测结果列表
detections.push_back(box);
// 输出部分检测结果用于调试
if (debug_count<4) {
std::cout<<“找到目标: 类别=”<<cls
<<” 置信度=”<<score
<<” 边界框=[“<<cx<<“, “<<cy<<“, “<<w<<“, “<<h<<“]”
<<std::endl;
debug_count++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
std::cout<<“特征图 “<<grid_h<<“x”<<grid_w<<” 共检测到 “
<<detections.size() <<” 个目标”<<std::endl;
}
void postprocess(cv::Mat& frame, const int num_boxes, const float* boxes, const float* confs, float conf_threshold, float nms_threshold, std::vector<Detection>& final_detections) {
vector<cv::Rect>temp_boxes;
vector<float>temp_confidences;
vector<int>temp_class_ids;
intorg_width=frame.cols;
intorg_height=frame.rows;
for(inti=0;i<num_boxes;i++){
// cv::Mat class_scores = scores.row(0).col(i);
std::vector<float>scores_list;
doubleconfidence=-1;
intclass_id=-1;
for(intj=0;j<80;j++){
// scores_list.push_back(confs[i*80+j]);
if(confs[i*80+j]>confidence){
confidence=confs[i*80+j];
class_id=j;
}
}
// cv::Mat class_scores(scores_list,false);
// cv::Point class_id_point;
// minMaxLoc(class_scores, 0, &confidence, 0, &class_id_point);
// int class_id = class_id_point.y;
if(confidence>conf_threshold){
intx=static_cast<int>(boxes[i*4+0]*org_width);
inty=static_cast<int>(boxes[i*4+1]*org_height);
intx2=static_cast<int>(boxes[i*4+2]*org_width);
inty2=static_cast<int>(boxes[i*4+3]*org_height);
cout<<“Box “<<i<<“: [“<<x<<“, “<<y<<“, “<<x2<<“, “<<y2<<“]”<<endl;
temp_boxes.push_back({cv::Point(x,y),cv::Point(x2,y2)});
temp_confidences.push_back(static_cast<float>(confidence));
temp_class_ids.push_back(class_id);
}
}
// 非极大值抑制
std::vector<int>indices;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(temp_boxes, temp_confidences, conf_threshold, nms_threshold, indices);
vector<cv::Rect>final_boxes;
vector<float>final_confidences;
vector<int>final_class_ids;
std::vector<Detection>detection_list;
for (intidx : indices) {
Detectiondet;
final_boxes.push_back(temp_boxes[idx]);
det.box.x=temp_boxes[idx].x;
det.box.y=temp_boxes[idx].y;
det.box.w=temp_boxes[idx].width;
det.box.h=temp_boxes[idx].height;
final_confidences.push_back(temp_confidences[idx]);
final_class_ids.push_back(temp_class_ids[idx]);
det.class_id=temp_class_ids[idx];
det.score=temp_confidences[idx];
detection_list.push_back(det);
}
cout<<“final_boxes: “;
for (constauto&box : final_boxes) {
cout<<“[“<<box.x<<“, “<<box.y<<“, “<<box.width<<“, “<<box.height<<“] “;
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<“final_confidences: “;
for (constauto&conf : final_confidences) {
cout<<conf<<” “;
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<“final_class_ids: “;
for (constauto&id : final_class_ids) {
cout<<id<<” “;
}
cout<<endl;
// draw_boxes(frame,detection_list);
}
static inline int64_t getCurrentTimeUs()
{
structtimevaltv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
returntv.tv_sec*1000000+tv.tv_usec;
}
uint32_t load_data(void *&inputBuff)
{
std::ifstreaminput_file(PIC, std::ifstream::binary);
if (input_file.is_open() ==false) {
ERROR_LOG(“open file %s failed”, PIC);
}
input_file.seekg(0, input_file.end);
uint32_tfile_szie=input_file.tellg();
if (file_szie==0) {
ERROR_LOG(“binfile is empty, filename is %s”, PIC);
input_file.close();
}
cout<<“————>file size “<<file_szie<<endl;
input_file.seekg(0, input_file.beg);
input_file.read(static_cast<char*>(inputBuff), file_szie);
input_file.close();
returnfile_szie;
}
int main()
{
/***************************************************/
/*****************Init ACL**************************/
/***************************************************/
cout<<“->ACL INIT “<<endl;
aclErrorret=aclInit(aclConfigPath);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“acl init failed, errorCode = %d”, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
/***************************************************/
/*****************apply resource********************/
/***************************************************/
// set device only one device
int32_tdeviceId_=0;
ret=aclrtSetDevice(deviceId_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“acl set device %d failed, errorCode = %d”, deviceId_, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->set device “<<deviceId_<<endl;
// create context (set current)
cout<<“->create context”<<endl;
aclrtContextcontext_;
ret=aclrtCreateContext(&context_, deviceId_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“acl create context failed, deviceId = %d, errorCode = %d”,
deviceId_, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
// create stream
cout<<“->create stream”<<endl;
aclrtStreamstream_;
ret=aclrtCreateStream(&stream_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“acl create stream failed, deviceId = %d, errorCode = %d”,
deviceId_, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
// get run mode
cout<<“->get run mode”<<endl;
aclrtRunModerunMode;
ret=aclrtGetRunMode(&runMode);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“acl get run mode failed, errorCode = %d”, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
g_isDevice=(runMode==ACL_DEVICE) ;
/***************************************************/
/********load model and get infos of model**********/
/***************************************************/
uint32_tmodelId_=0;
ret=aclmdlLoadFromFile(MODEL_PATH,&modelId_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“load model from file failed, model file is %s, errorCode is %d”,
MODEL_PATH, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->load mode “<<“\””<<MODEL_PATH<<“\””<<” model id is “<<modelId_<<endl;
//get model describe
cout<<“->create model describe”<<endl;
aclmdlDesc*modelDesc_;
modelDesc_=aclmdlCreateDesc();
if (modelDesc_==nullptr) {
ERROR_LOG(“create model description failed”);
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->get model describe”<<endl;
ret=aclmdlGetDesc(modelDesc_, modelId_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“get model description failed, modelId is %u, errorCode is %d”,
modelId_, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
deviceId_=0;
/***************************************************/
/******************prepare input data buffer********/
/***************************************************/
if (modelDesc_==nullptr) {
ERROR_LOG(“no model description, create input failed”);
returnFAILED;
}
cv::Matframe=cv::imread(PIC);
if (frame.empty()) {
ERROR_LOG(“read image failed, image path is %s”, PIC);
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->read image “<<PIC<<endl;
cv::Matresized_frame=preprocess_image(frame);
aclmdlDataset*input_;
void*inputDataBuffer=nullptr;
size_tmodelInputSize=aclmdlGetInputSizeByIndex(modelDesc_, 0);
cout<<“->get input size “<<modelInputSize<<endl;
cout<<“->apply input mem “<<endl;
aclErroraclRet=aclrtMalloc(&inputDataBuffer, modelInputSize, ACL_MEM_MALLOC_NORMAL_ONLY);
if (aclRet!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“malloc device buffer failed. size is %zu, errorCode is %d”,
modelInputSize, static_cast<int32_t>(aclRet));
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->copy data to device “<<endl;
ret=aclrtMemcpy(inputDataBuffer, modelInputSize, resized_frame.data, modelInputSize, ACL_MEMCPY_HOST_TO_DEVICE);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“copy data to device failed, errorCode is %d”, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
(void)aclrtFree(inputDataBuffer);
inputDataBuffer=nullptr;
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->copy data to device success “<<endl;
cout<<“->create input dataset “<<endl;
input_=aclmdlCreateDataset();
if (input_==nullptr) {
ERROR_LOG(“can’t create dataset, create input failed”);
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->create databuffer”<<endl;
aclDataBuffer*inputData=aclCreateDataBuffer(inputDataBuffer, modelInputSize);
if (inputData==nullptr) {
ERROR_LOG(“can’t create data buffer, create input failed”);
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->get input data buffer”<<endl;
size_tinputNum=aclmdlGetDatasetNumBuffers(input_);
cout<<“->get input dataset num “<<inputNum<<endl;
if (inputNum!=0) {
ERROR_LOG(“dataset buffer num is not 0, create input failed”);
(void)aclDestroyDataBuffer(inputData);
inputData=nullptr;
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->get input data buffer success “<<endl;
cout<<“->add data to datasetbuffer”<<endl;
ret=aclmdlAddDatasetBuffer(input_, inputData);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“add input dataset buffer failed, errorCode is %d”, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
(void)aclDestroyDataBuffer(inputData);
inputData=nullptr;
returnFAILED;
}
INFO_LOG(“create model input success”);
/***************************************************/
/************prepare output data buffer*************/
/***************************************************/
aclmdlDataset*output_;
cout<<“->create dataset”<<endl;
output_=aclmdlCreateDataset();
if (output_==nullptr) {
ERROR_LOG(“can’t create dataset, create output failed”);
returnFAILED;
}
size_toutput_num=aclmdlGetNumOutputs(modelDesc_);
cout<<“->get num of output “<<output_num<<endl;
for (size_ti=0; i<output_num; ++i) {
size_tmodelOutputSize=aclmdlGetOutputSizeByIndex(modelDesc_, i);
cout<<“-> output size[“<<i<<“] :”<<modelOutputSize<<endl;
void*outputBuffer=nullptr;
aclErrorret=aclrtMalloc(&outputBuffer, modelOutputSize, ACL_MEM_MALLOC_NORMAL_ONLY);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“can’t malloc buffer, size is %zu, create output failed, errorCode is %d”,
modelOutputSize, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
//apply output buffer
cout<<“->apply output buffer”<<endl;
aclDataBuffer*outputData=aclCreateDataBuffer(outputBuffer, modelOutputSize);
if (outputData==nullptr) {
ERROR_LOG(“can’t create data buffer, create output failed”);
(void)aclrtFree(outputBuffer);
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“->AddDatasetBuffer”<<endl;
ret=aclmdlAddDatasetBuffer(output_, outputData);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“can’t add data buffer, create output failed, errorCode is %d”,
static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
(void)aclrtFree(outputBuffer);
(void)aclDestroyDataBuffer(outputData);
returnFAILED;
}
cout<<“-> get original output test”<<endl;
aclDataBuffer*dataBuffer=aclmdlGetDatasetBuffer(output_, i);
void*data=aclGetDataBufferAddr(dataBuffer);
uint32_tlen=aclGetDataBufferSizeV2(dataBuffer);
cout<<“-> getDataBufferSizeV2[“<<i<<“] :”<<len<<endl;
float*outData=NULL;
outData=reinterpret_cast<float*>(data);
for(intnum=0;num<10;num++){
cout<<outData[num]<<endl;
}
}
cout<<“->create model output success “<<endl;
/***************************************************/
/******************inference************************/
/***************************************************/
// for(int i=0;i<100000;i++){
cout<<“->begin inference “<<“model id is “<<modelId_<<endl;
int64_tsum=0;
int64_tstart_time=0;
int64_tend_time=0;
int64_teclipes_time=0;
// for(int i = 0; i < loop_count;i++){
start_time=getCurrentTimeUs();
//ret = aclmdlExecuteAsync(modelId_, input_, output_,stream_);
ret=aclmdlExecute(modelId_, input_, output_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“execute model failed, modelId is %u, errorCode is %d”,
modelId_, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
end_time=getCurrentTimeUs();
eclipes_time=end_time-start_time;
// if(i!=0){
// sum =sum + eclipes_time;
// }
printf(“——————use time %.2f ms\n”, eclipes_time/1000.f);
// }
// }
// printf(“loop %d averages use time %.2f ms\n”,loop_count-1,(sum/1000.f)/(loop_count-1));
/***************************************************/
/******************post process*********************/
/***************************************************/
std::vector<cv::Mat>output_list=parseAclOutput(output_);
std::vector<int>output_shape;
aclFormatformat;
std::vector<constchar*>output_names;
aclDataTypedata_type;
intnum_boxes;
intnum_classes;
for(intnum=0;num<(int)output_num;num++){
constchar*output_name;
size_toutput_stride;
uint32_tlen ;
aclmdlIODimsdims;
output_shape.clear();
aclmdlGetOutputDims(modelDesc_, num,&dims);
output_name=aclmdlGetOutputNameByIndex(modelDesc_,num);
output_names.push_back(output_name);
format=aclmdlGetOutputFormat(modelDesc_,num);
data_type=aclmdlGetOutputDataType(modelDesc_,num);
aclDataBuffer*dataBuffer=aclmdlGetDatasetBuffer(output_, num);
void*data=aclGetDataBufferAddr(dataBuffer);
len=aclGetDataBufferSize(dataBuffer);
cout<<“->dims [ “;
for(intdim_num=0;dim_num<(int)dims.dimCount;dim_num++){
cout<<dims.dims[dim_num]<<” “;
output_shape.push_back(dims.dims[dim_num]);
}
cout<<“] output format is “<<format<<” data_type is”<<data_type<<” output_stride is “<<output_stride<<” output_name is “<<output_names[num]<<“-> getDataBufferSize[“<<num<<“] :”<<len<<endl;
if(num==0){
num_boxes=output_shape[1];
}else{
num_classes=output_shape[2];
}
float*outData=NULL;
outData=reinterpret_cast<float*>(data);
//show output data
// for(int show_num=0;show_num<0;show_num++){
// printf(“%f \n”,outData[show_num]);
// }
}
// yolov5的结果集为[1,3,80,80,85] [1,3,40,40,85] [1,3,20,20,85] 下面对这个结果集进行处理
// 这里添加处理YOLOv5结果集的代码
// 获取三个输出特征图
constfloat*feature_map1=nullptr;
constfloat*feature_map2=nullptr;
constfloat*feature_map3=nullptr;
// 遍历输出数据集,获取特征图
std::vector<cv::Mat>feature_maps;
for (size_ti=0; i<aclmdlGetDatasetNumBuffers(output_); ++i) {
aclDataBuffer*buffer=aclmdlGetDatasetBuffer(output_, i);
void*data=aclGetDataBufferAddr(buffer);
if (i==0) {
feature_map1=reinterpret_cast<float*>(data); // 80×80
} else if (i == 1) {
feature_map2=reinterpret_cast<float*>(data); // 40×40
} else if (i == 2) {
feature_map3=reinterpret_cast<float*>(data); // 20×20
}
}
// 处理参数
constfloatconf_threshold=0.5f; // 置信度阈值
constfloatnms_threshold=0.45f; // NMS阈值
constintinput_width=640; // 输入图像宽度
constintinput_height=640; // 输入图像高度
// 确保创建一个全局向量存储所有检测结果
std::vector<Box>all_detections;
// 处理三个特征图
std::vector<Box>detections_80x80;
processFeatureMap(feature_map1, detections_80x80, 80, 80, 3, 85, conf_threshold, input_width, input_height);
std::vector<Box>detections_40x40;
processFeatureMap(feature_map2, detections_40x40, 40, 40, 3, 85, conf_threshold, input_width, input_height);
std::vector<Box>detections_20x20;
processFeatureMap(feature_map3, detections_20x20, 20, 20, 3, 85, conf_threshold, input_width, input_height);
// 合并所有检测结果
all_detections.insert(all_detections.end(), detections_80x80.begin(), detections_80x80.end());
all_detections.insert(all_detections.end(), detections_40x40.begin(), detections_40x40.end());
all_detections.insert(all_detections.end(), detections_20x20.begin(), detections_20x20.end());
std::cout<<“所有特征图总共检测到 “<<all_detections.size() <<” 个目标”<<std::endl;
// 执行NMS
std::vector<DetectionResult>final_detections=nms_boxes(all_detections, nms_threshold, conf_threshold);
// 输出最终结果
std::cout<<“最终检测到 “<<final_detections.size() <<” 个目标”<<std::endl;
cv::Matimg=cv::imread(“data/output2.jpg”);
draw_boxes(img,final_detections);
cv::imwrite(“result.jpg”,img);
/***************************************************/
/*********************destroy model output*********/
/***************************************************/
for (size_ti=0; i<aclmdlGetDatasetNumBuffers(output_); ++i) {
aclDataBuffer*dataBuffer=aclmdlGetDatasetBuffer(output_, i);
void*data=aclGetDataBufferAddr(dataBuffer);
(void)aclrtFree(data);
(void)aclDestroyDataBuffer(dataBuffer);
}
(void)aclmdlDestroyDataset(output_);
output_=nullptr;
INFO_LOG(“destroy model output success”);
/***************************************************/
/*******************destroy model input*************/
/***************************************************/
for (size_ti=0; i<aclmdlGetDatasetNumBuffers(input_); ++i) {
aclDataBuffer*dataBuffer=aclmdlGetDatasetBuffer(input_, i);
(void)aclDestroyDataBuffer(dataBuffer);
}
(void)aclmdlDestroyDataset(input_);
input_=nullptr;
INFO_LOG(“destroy model input success”);
/***************************************************/
/******uninstall model and release resource*********/
/***************************************************/
cout<<“->unload model id is “<<modelId_<<endl;
ret=aclmdlUnload(modelId_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“unload model failed, modelId is %u, errorCode is %d”,
modelId_, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
returnFAILED;
}
INFO_LOG(“unload model success, modelId is %u”, modelId_);
// releasemodelDesc_
if (modelDesc_!=nullptr) {
aclmdlDestroyDesc(modelDesc_);
modelDesc_=nullptr;
}
INFO_LOG(“release modelDesc_ success, modelId is %u”, modelId_);
//release resorce
if (stream_!=nullptr) {
ret=aclrtDestroyStream(stream_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“destroy stream failed, errorCode = %d”, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
}
stream_=nullptr;
}
cout<<“->destroy stream done”<<endl;
if (context_!=nullptr) {
ret=aclrtDestroyContext(context_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“destroy context failed, errorCode = %d”, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
}
context_=nullptr;
}
cout<<“->destroy context done “<<endl;
ret=aclrtResetDevice(deviceId_);
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(“reset device %d failed, errorCode = %d”, deviceId_, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
}
cout<<“->reset device id is “<<deviceId_<<endl;
ret=aclFinalize();
if (ret!=ACL_SUCCESS) {
ERROR_LOG(” failed, errorCode = %d”, static_cast<int32_t>(ret));
}
INFO_LOG(“end to finalize acl”);
}